Union forces built the main dam near the river's lower rapids. The dam had three parts that worked as a whole. These were 1) a tree dam on the east bank of the river, 2) a series of cribs (boxes) on the west bank, and 3) a section in the middle made of four sunken coal barges anchored to the dams. The barges filled a 150-foot gap between the tree dam and the crib dam. Together, these parts forced water into a central, rapidly flowing channel.
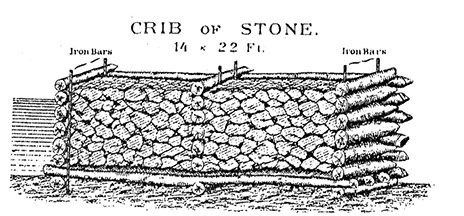
Two USCT regiments were instrumental in building the dam on the west bank of the river. This part was made of a row of boxes known as "cribs of stone." The picture shows that the boxes were filled with stone and held in place with iron bars. Historical accounts say that soldiers put bricks, stone and machinery in the dams. However, archaeologists found that they mainly used sand and mud in the crib dam and only placed brick and stone on the top. Sketch of crib dam, which accompanied Colonel Bailey's report (U.S. War Department 1891-1895: Plate 53-3).

On the east side of the river, a Maine regiment cut down trees from nearby forests to build the tree dam. Like the cribs, soldiers weighed the tree dam down with stones and bricks. The diagram shows that the trees were placed with their tops going upstream and the trunks pointing downstream. During fieldwork, archaeologists found that the actual direction of the trees was opposite from that shown in the drawing. Still, the picture gives a good overview of a tree dam. Sketch of tree dam, which accompanied Colonel Bailey's report (U.S. War Department 1891-1895: Plate 53-3).
Next
Back
While 28 military units helped build the dam, the majority of the work was done by three crews. The 29th Maine Volunteer Infantry Regiment worked on the east side of the river, closest to Pineville. Freed slaves in the 97th Regiment and the 99th Regiment of the United States Colored Troops (USCT) Infantry worked on the Alexandria side of the river.